Accessibility Checklist
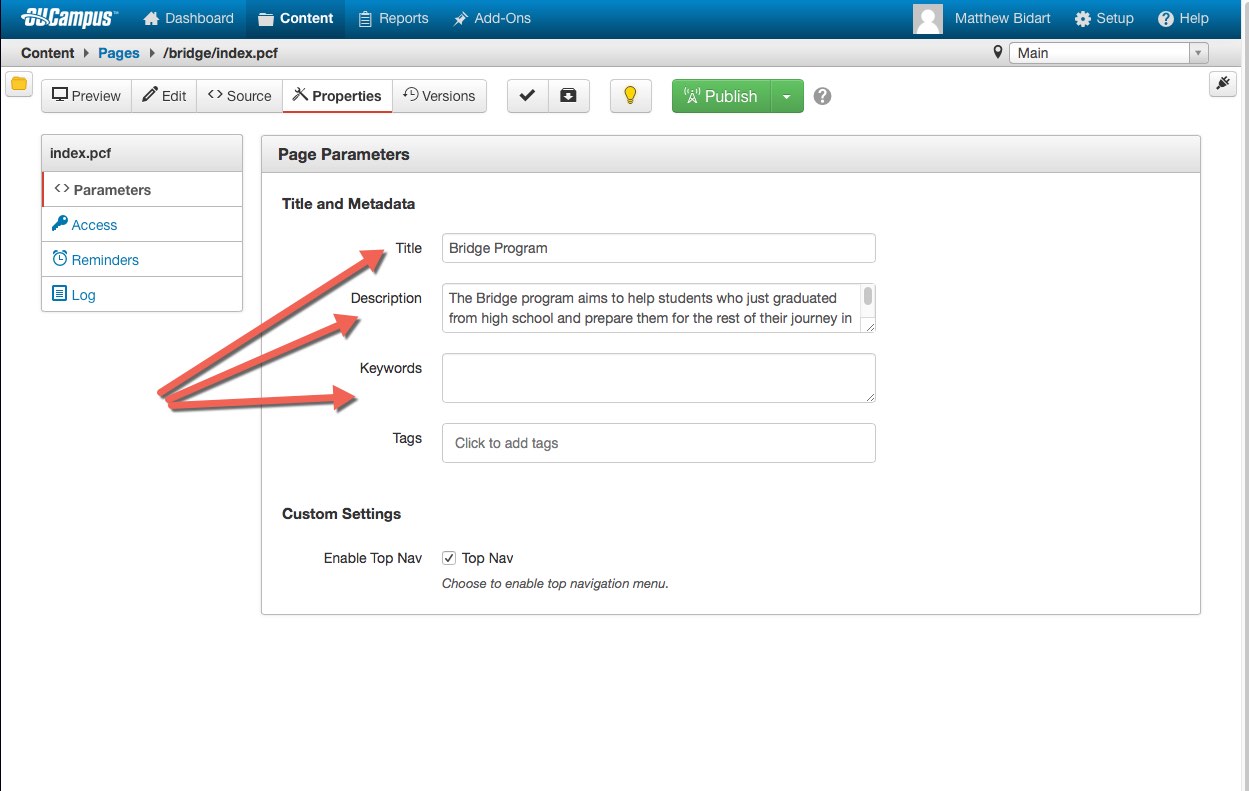
 Page Title and Description
Page Title and Description
Page Title
- Defines title of a web document; should be unique with a consistent format site-wide
- Less than 70 characters
- Shows in Google search results and browser title bar (also default text for bookmark)
- Use meaningful words; avoid vague acronyms with no first reference or context (e.g.
“MCM” for Master of Contemporary Music) that may alienate or confuse both the user
and search engines, unless the acronym is commonly understood by target audience (e.g.
MBA)
- Echo keywords used in the page description. Balance use of keywords with compelling,
descriptive language so both humans and machines can make sense of information
- Place keywords near front of title (Primary Keyword- Secondary Keyword | Brand Name)
Page (Meta) Description
- Add a unique page description that describes the content found on your page
- Maximum of 150-160 characters
- Strong descriptions can boost traffic from search engine result pages (SERPs)
- Echo keywords used in the title; balance keywords with compelling, descriptive language
so both humans and machines can make sense of information
- Avoid quotes stick to alphanumeric characters
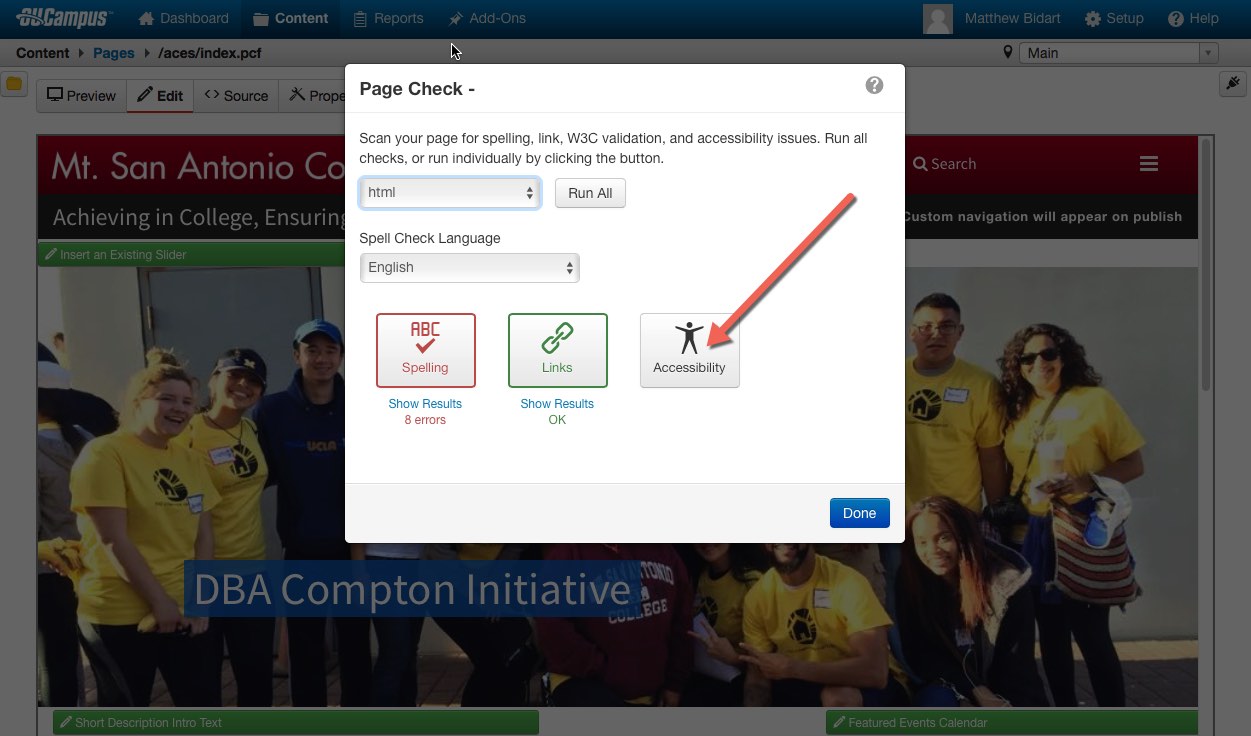
Scan Your Pages
- Automated scans can successfully find many accessibility issues
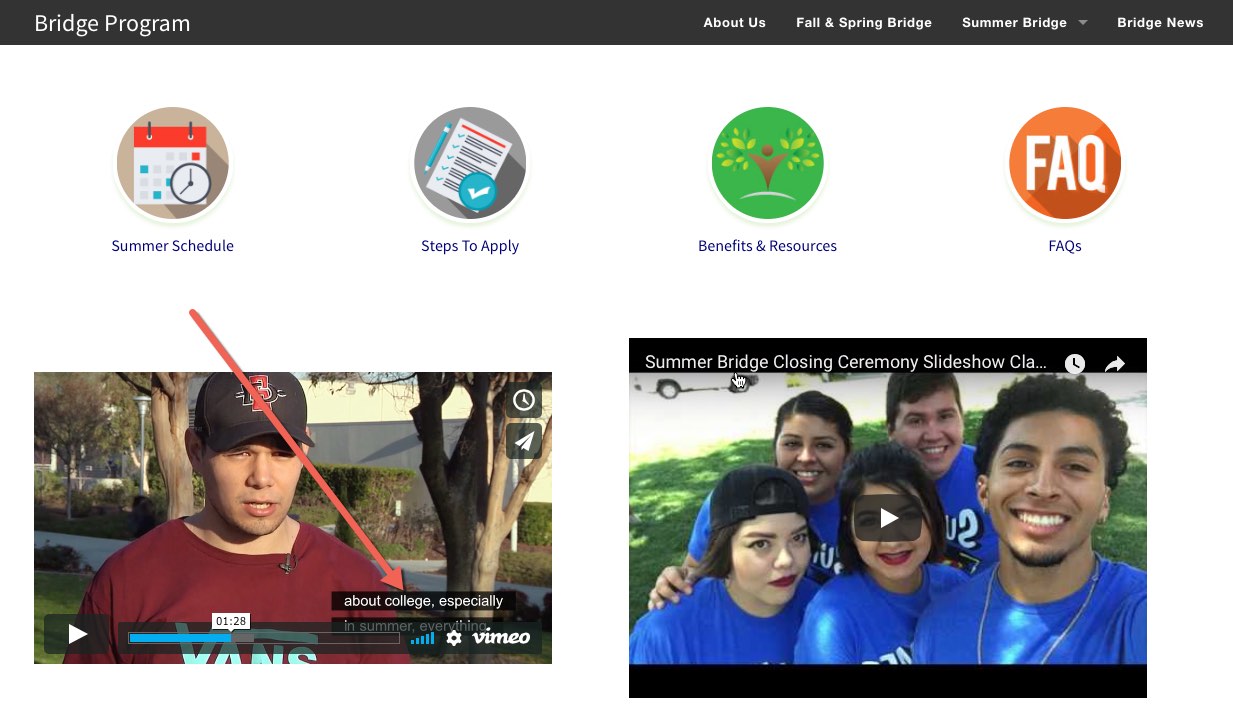
Check Images
- Always use alt text for images to allow non-sighted users using “talking” browsers,
as well as users on slow connections, to glean meaning from image content
- Describe what is happening in the image (e.g. “Students studying in a library”)
- Alt text has the bonus of being searchable, enhancing SEO
-
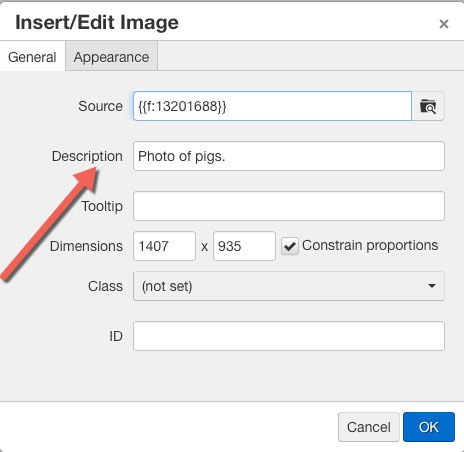
- How to check images for alternative text
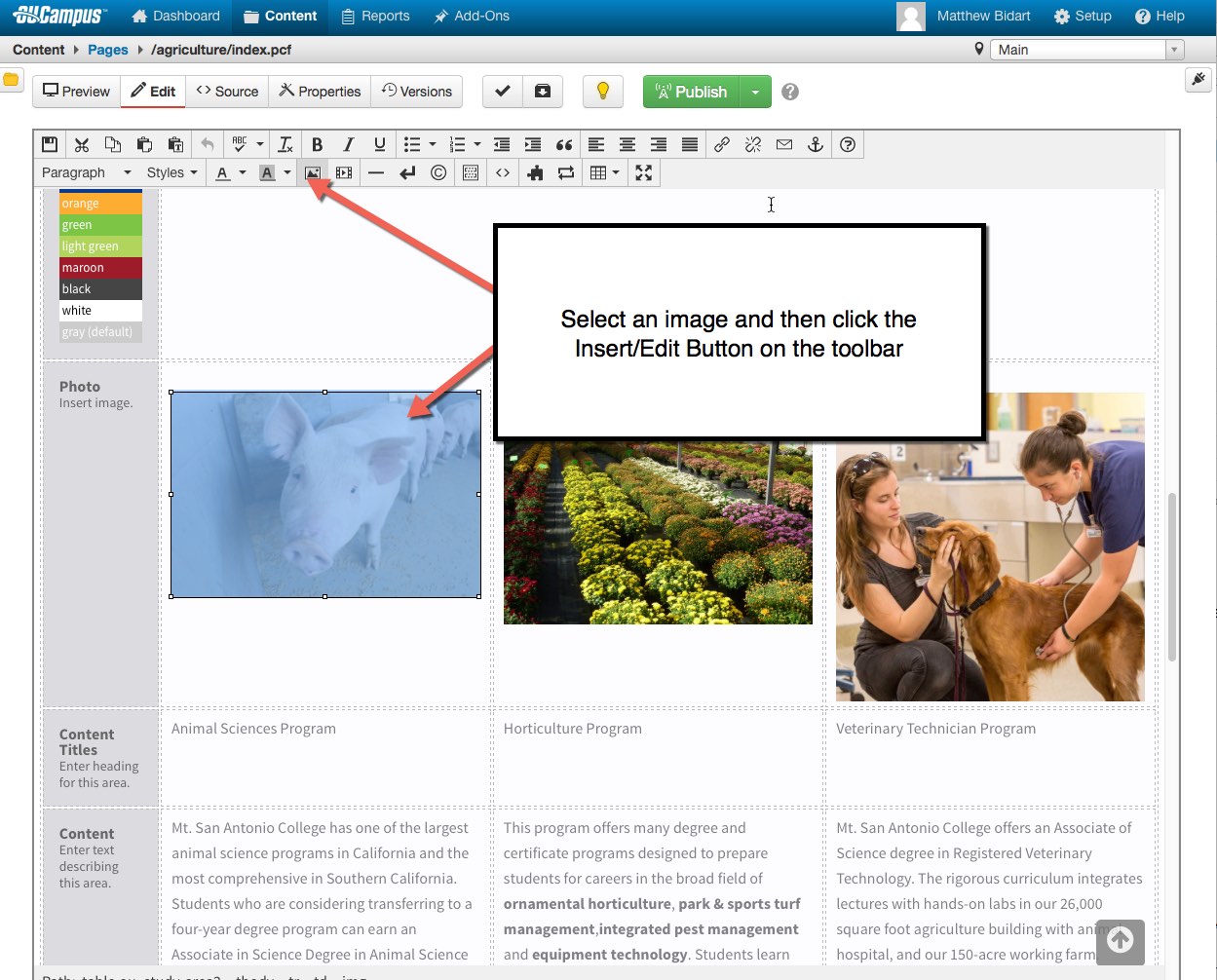
- Navigate to your page within OmniUpdate
- Check Out the page
- Click the Edit button for regions with images
- Click the image to select it
- Click the Insert/Edit button
- Edit/Update the image Description
Links
- Make links descriptive and actionable (e.g. “Apply now”; “View event calendar”). Links
should clearly show where they go
- The words “click here” have no value for search engines, or for users
- Use simple URL structures; 3-5 words
- Use hyphens instead of underscores
- Test links to make sure they go to the desired place
Videos
- Due to our educational and commercial-free content, the Mt. SAC Vimeo.com video service is recommended over YouTube.
- Make sure your videos are Closed Captioned. Please use these resources:
Tab Navigation
- Test your page to make sure all navigation works by using the Tab and/or Space Bar
keys
-
- How to check tab navigation
- Once your page loads
- Press the Tab key. Confirm the desired navigation is achieved
- Continue to press the Tab key, stopping between presses to confirm the desired navigation
is achieved
Hierarchical Heading Order
- HTML heading tags help create hierarchies by organizing, prioritizing and labeling
content. Use headings with clear, descriptive language to break up text and guide
readers scanning the page
- Headings and Subheadings must be laid out in a logical and hierarchical order. Heading
1 (H1) should appear at the top followed by subheadings
- Heading 3 (H3) should not appear on the page if there is not a Heading 2 (H2) above
it
Form Navigation
- Forms must be able to be navigated using the Tab and Enter keys
-
- How to check form navigation
- Once your page loads
- Press the Tab key. Confirm the cursors moves to the next logical entry point
- Also, test if you click a label, does the cursor move to the corresponding entry point
PDF Documents
Other Tips
- Avoid directional language (e.g. read below, see above, the menu to the left) when
referring to on-page content
- Due to responsive design, “on the right” in one context may be “below” in another
- Do not rely solely on a visual or audio communication (imagery, shape, size, sound)
to communicate information that is critical to comprehending content
 Page Title and Description
Page Title and Description