Making Your Microsoft Word Document Accessible
The first step is to scan for accessibility errors/issues using Microsoft Word:
- Open the document in Microsoft Word
- Open the File menu
- Click the Check for Issues button
- Click Check Accessibility
Correcting Accessible Issues in Word
If any accessibility issues are found:
- Click each issue in the Accessibility Pane
- Correct the issue.
Creating Accessible Word Documents from Scratch
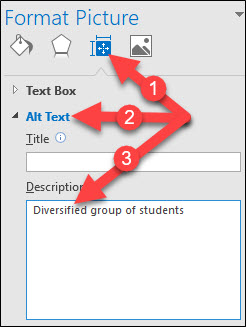
Microsoft Word documents can be made accessible by following the LIST model (Links, Images, Structure and Style) recommended by the High Tech Center Training Unit/Access Center as described below. Navigate through your document and address all of the following for accessibility issues.
Other Considerations
Next, scan the document using the Accessibility Checker to make sure your document meets WCAG accessibility standards.